The Retail & Consumer Insights Blog

Urban Farming Trends in Compact City Spaces
For common city dwellers, this means concrete, high-rises, and a lack of green space. However, as populations shift to cities and climate concerns loom, so does urban farming. Once considered a niche pursuit, it has become a vital, sustainable source of food for people living in cities across the globe.
Many people seek to grow food at home in our small urban spaces. Rooftop gardens and vertical hydroponic systems allow city dwellers to reconnect with natural biodiversity. They also support people in taking ownership of food production. This blog shares the exciting urban farming trends that are changing city life. It also covers the environmental, social, and economic benefits they bring. Read on if you’re interested in sustainable lifestyles, healthy eating, or adding some greenery to your urban home.
Why Urban Farming Matters
A Response to Food Insecurity
Many urban areas, especially low-income neighbourhoods, struggle to access fresh, affordable food. Known as “food deserts,” these regions have led to local initiatives aimed at producing food nearby. Urban farming shortens the supply chain and empowers communities to regain control over their food sources.
Sustainable Food Solutions
Transporting food from rural farms to city supermarkets adds to greenhouse gas emissions. Locally grown produce significantly cuts this impact. Urban farms use methods that save water and require less land, making them more sustainable.
Mental Health and Community Building
Research shows that gardening boosts mental well-being. Urban farming projects, like community gardens, increase mindfulness and lower stress. They also help build stronger connections in neighbourhoods. They serve as hubs for education, collaboration, and collective growth.
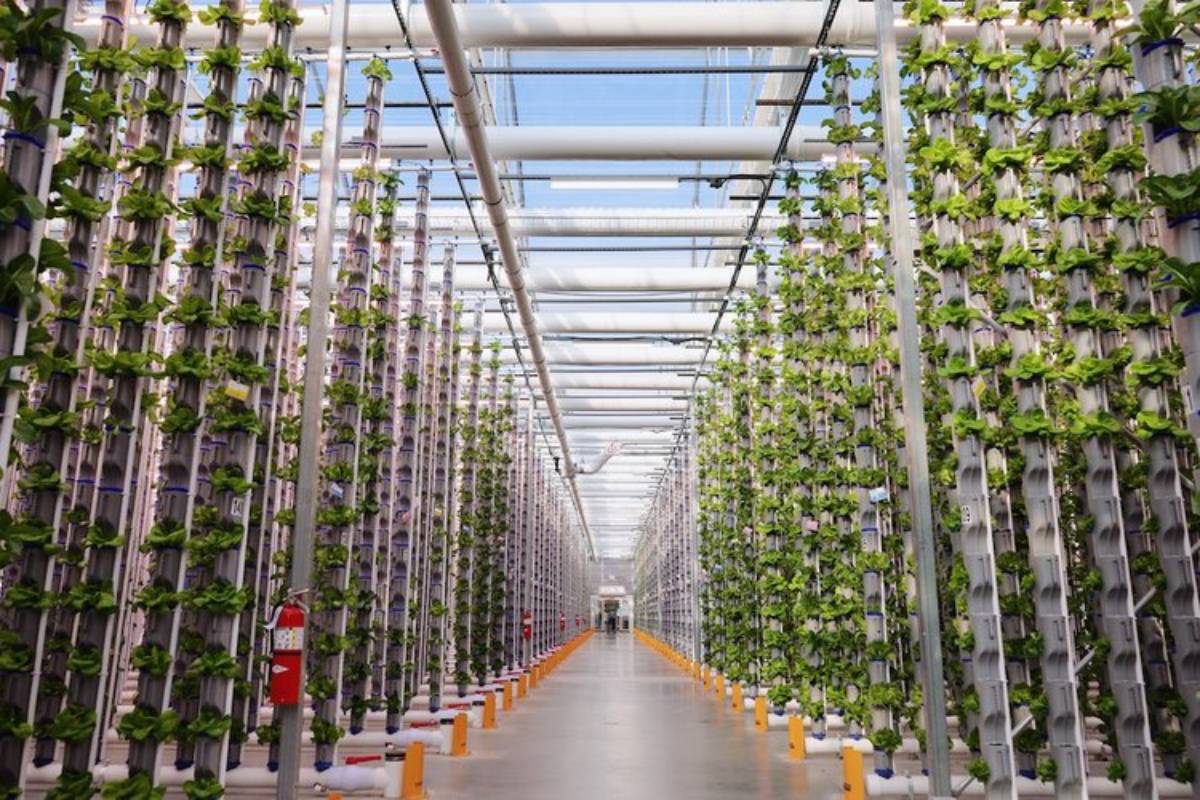

Trend 1: Vertical Farming
What Is Vertical Farming?
Vertical farming grows crops in stacked layers, often inside buildings or shipping containers. It uses controlled environments and soil-less systems, like hydroponics and aeroponics. This means it can produce crops year-round, no matter the climate.
Real-World Example: Plenty & Infarm
Infarm is a Berlin start-up. Plenty is a California company that creates large vertical farms. These farms provide fresh produce to major grocery chains. They install modular vertical farms in supermarkets and restaurants, which helps with hyper-local food production.
Benefits:
- Maximises space efficiency in tight areas
- Reduces water use by up to 95%
- Minimises pesticides and chemicals
- Shortens the farm-to-fork cycle
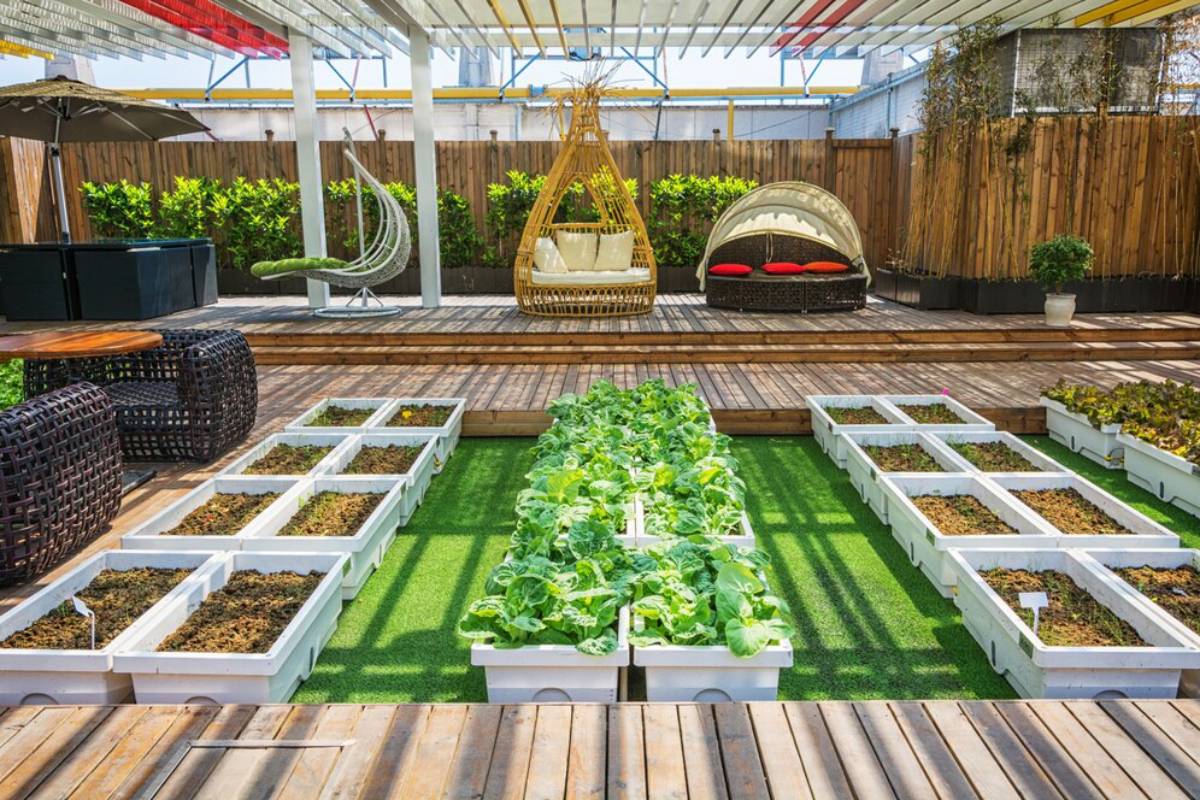

Trend 2: Rooftop Gardens
Turning Rooftops Into Edible Landscapes
Urban rooftops are becoming productive green spaces. These gardens vary from simple planters to elaborate greenhouses with aquaponic systems.
Case Study: Brooklyn Grange, New York
Brooklyn Grange is one of the world’s largest rooftop soil farms, growing over 22,000 kilograms of produce each year. They also host community events and educational programs.
Key Benefits:
- Improves air quality and building insulation
- Creates habitats for pollinators
- Reduces urban heat islands
- Fosters community involvement
Trend 3: Indoor Hydroponics and Smart Systems
Farming Without Soil
Hydroponic systems grow plants in nutrient-rich water solutions. Smart technology lets you control temperature, humidity, and light precisely, making indoor farming more efficient.
At-Home Systems
Compact hydroponic units, such as AeroGarden and Rise Gardens, help apartment dwellers grow herbs and veggies. They can do this right in their kitchens or living rooms.
Technological Advancements:
- IoT integration for real-time monitoring
- Automated lighting and nutrient delivery
- Energy-efficient LED grow lights
Trend 4: Community Gardens and Urban Allotments
Bringing People Together Through Growing
While individual systems offer convenience, community gardens provide shared spaces for collaboration. These green areas often revitalise neglected lots and become valuable community assets.
Local Impact: Incredible Edible, UK
Incredible Edible began in Todmorden and spread across the UK. It encourages planting edible crops in public spaces, promoting fresh food access and community spirit.
Key Advantages:
- Encourages inclusive urban regeneration
- Educates residents about growing and nutrition
- Promotes environmental awareness

Trend 5: Edible Landscaping and Guerrilla Gardening
Blurring the Line Between Ornamental and Edible
Edible landscaping mixes food-producing plants into traditional garden designs. It can be found in front yards, along sidewalks, and even in business parks.
Guerrilla Gardening
This form of activism involves planting in neglected spaces without formal permission. It aims to reclaim land for the public good.
Examples of Edible Plants Used:
- Fruit trees
- Berry bushes
- Herb spirals and edible flowers
Trend 6: Container Gardening for Micro-Spaces
Growing in Small Places
Cultivate food even in tiny apartments. Containers, window boxes, and hanging planters provide flexibility and mobility.
Ideal Plants for Containers:
- Tomatoes
- Chillies
- Basil and mint
- Strawberries
Tips for Success:
- Choose the right container size
- Use quality potting soil
- Ensure adequate sunlight or grow lights
Common Challenges and Solutions
Limited Sunlight
Urban buildings often block sunlight. Solutions include:
- South-facing windows
- LED grow lights
- Reflective surfaces to enhance light
Pollution and Contaminated Soil
Raised beds, container gardening and soil testing help ensure clean, safe growth.
Time and Maintenance
Smart tech and automated systems lessen the time needed for indoor or balcony farms.
The Future of Urban Agriculture
Policy and Infrastructure Support
Governments and city planners are starting to recognise the value of urban agriculture. Incentives, zoning changes, and grants can help grow these projects.
Integration With Architecture
New designs now include green walls, rooftop farms, and shared garden spaces in homes and businesses.
Education and Engagement
More schools and universities are adding urban agriculture to their programs. This helps future generations appreciate sustainability.
Sowing Seeds for a Greener Tomorrow
Urban farming is no longer a fringe movement; it’s a realistic, critical solution to the urban dilemmas of the day. Many city food-growing initiatives exist, from high-tech vertical farms to terrace gardens. It keeps money in local economies and creates community spirit. By adapting to these urban farming trends, we can all contribute to a healthier urban future.
If you have a rooftop or a sunny windowsill, there’s a way for you to get in on the action. Start small, play around and let us know how it goes. The future of city living is green, local, and rooted in sustainable food solutions.
Ready to start your urban farming journey? Explore container garden kits, join a local community garden, or try a hydroponic system. Every step counts towards a more self-sufficient and healthier lifestyle.