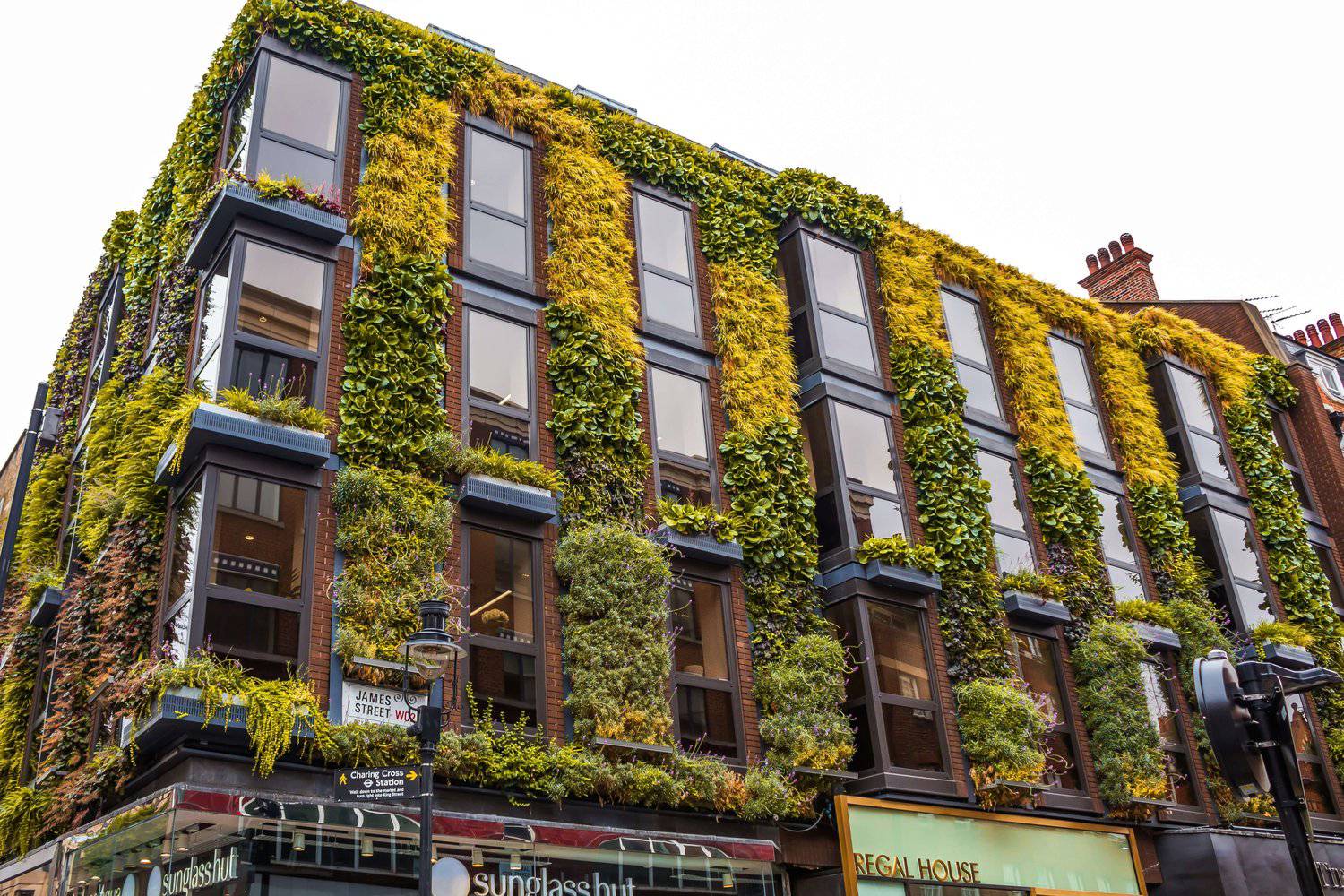
Vertical Gardens: The Future of Green Urban Spaces
As cities grow and become more crowded, the need for green infrastructure is more important than ever. In the city’s concrete and steel, vertical gardens are popping up. They offer a new way to live sustainably. Vertical gardens bring beauty and function to buildings by adding vegetation to their walls. This helps reconnect nature with urban areas.
More than just decorative installations, vertical gardens provide tangible environmental and social benefits. Living walls are changing green architecture. They help reduce the urban heat island effect, improve air quality, and boost biodiversity. This blog looks at why vertical gardens matter. It highlights their benefits and future potential. Vertical gardens can turn urban spaces into green oases.
Why It Matters
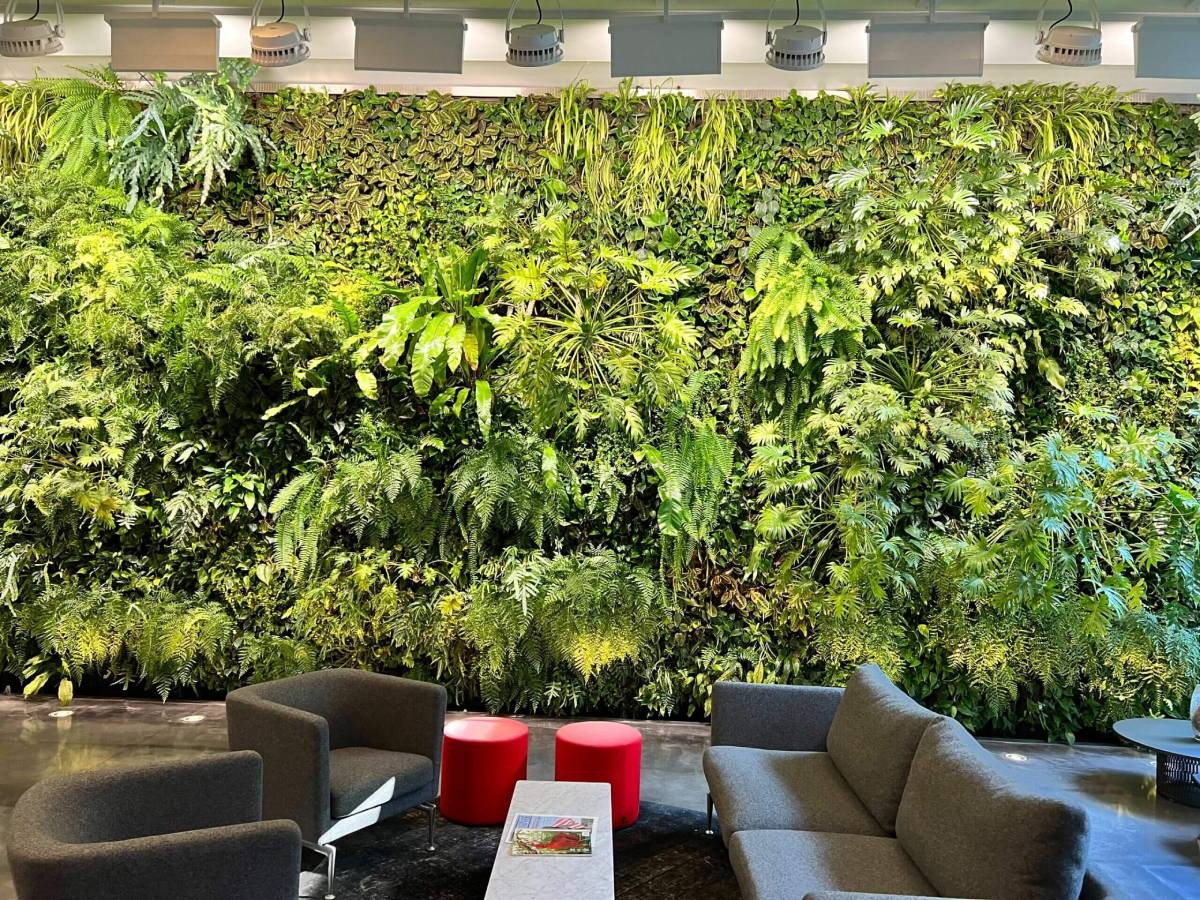

1. Environmental Sustainability
Vertical gardens play a pivotal role in promoting environmental sustainability in urban areas. By incorporating vegetation into building facades, they help:
- Combat air pollution: Plants filter out harmful pollutants like carbon dioxide and tiny particles. This helps improve air quality.
- Lower heat absorption: Green walls insulate buildings. This cuts the need for air conditioning and saves energy.
- Promote biodiversity: Vertical gardens provide homes for birds, bees, and insects. This helps boost biodiversity in cities.
2. Reducing the Urban Heat Island Effect
Urban areas often experience the heat island effect. This happens when buildings and pavements soak up and release heat. As a result, temperatures rise. Vertical gardens help counteract this by:
- Providing natural insulation: The vegetation absorbs heat and cools the surrounding air.
- Reducing energy consumption: By lowering indoor temperatures, vertical gardens reduce the need for air conditioning, resulting in energy savings.
- Mitigating heat stress: Cooler temperatures help public health by lowering heat-related illnesses.
3. Enhancing Air Quality
Vertical gardens act as natural air purifiers, filtering pollutants and releasing oxygen. Their benefits include:
- Capturing CO2: Plants absorb carbon dioxide during photosynthesis, helping reduce greenhouse gases.
- Filtering toxins: Green walls catch dust, allergens, and harmful chemicals. This helps to boost air quality in city areas.
- Reducing noise pollution: Plants serve as a sound barrier. They absorb and deflect noise.
4. Aesthetic and Psychological Benefits
Beyond their environmental advantages, vertical gardens offer aesthetic and psychological benefits by:
- Beautifying urban spaces: Living walls bring beauty, making green spots in grey areas.
- Improving mental well-being: Green spaces help lower stress and boost mood, which supports mental health.
- Enhancing property value: Buildings with vertical gardens often have higher property values and greater appeal to eco-conscious buyers.
5. Space-Efficient Gardening
For city dwellers with little space, vertical gardens offer a smart way to garden efficiently.
- Maximising small spaces: Vertical gardens are perfect for apartments, balconies, and courtyards. They help city dwellers grow plants in limited areas.
- Urban farming potential: Vertical farms grow food in cities. They boost local agriculture and cut down the carbon footprint from food transport.
Step-by-Step Guide to Creating Vertical Gardens
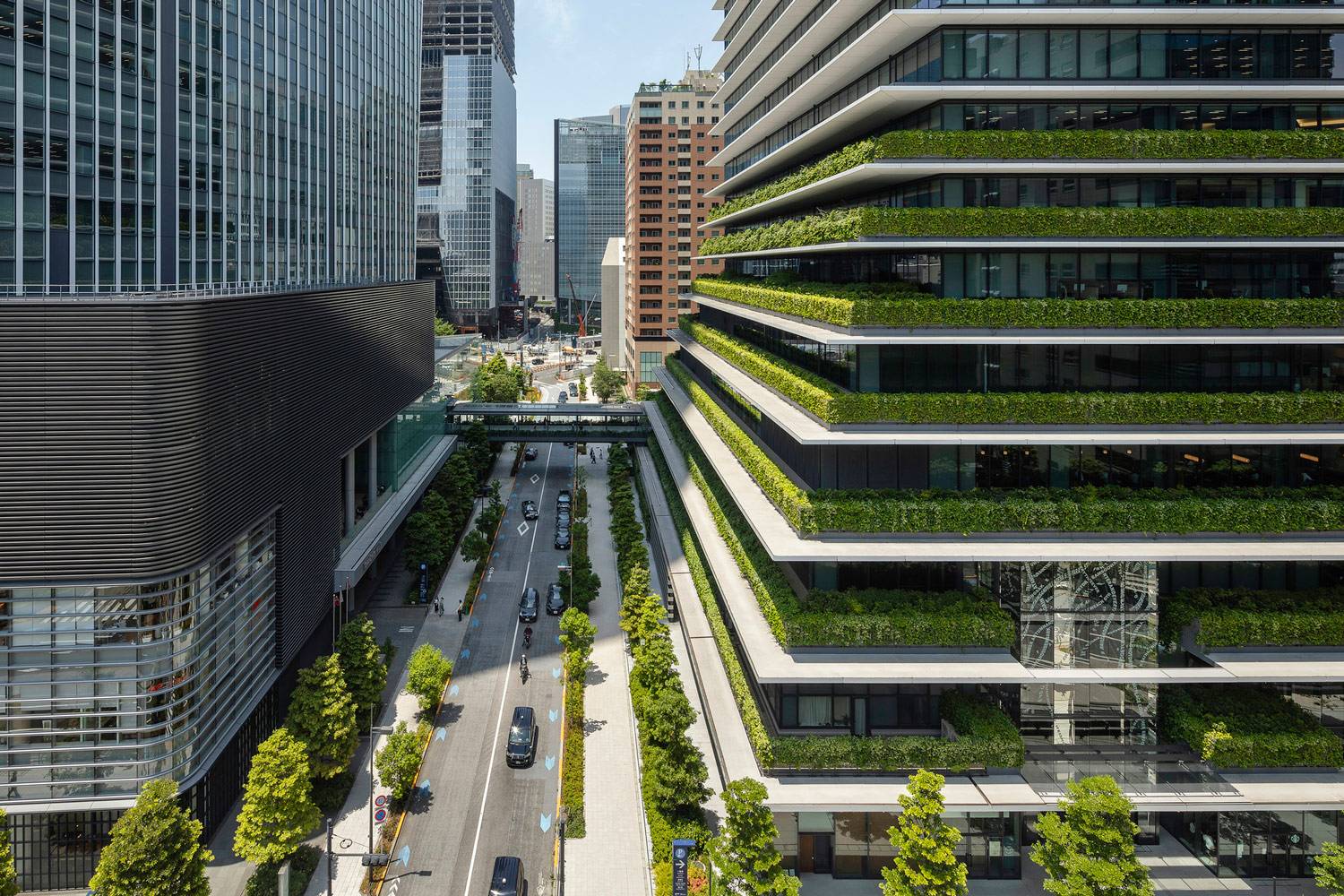

Step 1: Assess Your Space and Environment
Before starting a vertical garden, evaluate the available space and consider environmental factors:
- Sunlight exposure: Check how much sunlight the area gets each day. This helps choose the right plants.
- Wind conditions: Think about if the spot faces strong winds. This can impact how plants grow.
- Structural integrity: Make sure the wall or frame can hold the weight of the garden and irrigation system.
Step 2: Select the Right Plants
Choosing the right plants is essential for longevity and visual appeal. Consider the following:
- Climate suitability: Opt for plants that thrive in your region’s climate conditions.
- Low-maintenance plants: Choose hardy options like ferns, succulents, and trailing vines. They need little care.
- Biodiversity: Incorporate a variety of plants to enhance visual diversity and promote biodiversity.
Step 3: Choose a Vertical Garden System
There are several types of vertical garden systems to choose from, including:
- Modular panels: Pre-planted panels with integrated irrigation systems, ideal for larger installations.
- Pocket systems: Fabric pockets that hold individual plants, suitable for small-scale projects.
- Trellis systems: Frames that support climbing plants, perfect for outdoor walls and fences.
Step 4: Install the Vertical Garden
Once you have chosen the system, follow these steps for installation:
- Prepare the wall: Make sure the surface is clean, dry, and strong enough to support the garden’s weight.
- Attach the frame or panel: Fix the garden structure to the wall with strong brackets or support systems.
- Install the irrigation system: Automated drip or hydroponic systems provide steady watering and lower upkeep.
- Add the plants: Gently put the plants in the system. Make sure they have enough space to grow.
Step 5: Maintain and Care for Your Vertical Garden
Regular maintenance is essential to keep your vertical garden healthy:
- Watering: Check the irrigation system. Make sure plants get enough water.
- Pruning and trimming: Cut away dead leaves. Trim overgrown plants to keep everything looking tidy.
- Fertilising: Use organic fertilisers to provide essential nutrients for plant growth.
Additional Expert Tips & Common Mistakes to Avoid
Expert Tips
- Use native plants: They fit the local climate well, so they are easier to care for and more sustainable.
- Add edible plants: Grow herbs, strawberries, or leafy greens in your vertical garden. This way, you can enjoy a small-scale urban farm.
- Enhance irrigation efficiency: Use moisture sensors to optimise water usage and prevent overwatering.
- Add lighting for aesthetics: Use LED or solar lights to brighten your garden at night. This will enhance its visual charm.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Neglecting structural integrity: Ensure the building or wall can support the weight of the garden to prevent damage.
- Inadequate irrigation: Inconsistent watering can lead to plant stress and uneven growth.
- Choosing the wrong plants: Avoid plants that require intensive maintenance or are ill-suited to the environment.
- Overcrowding: Ensure proper plant spacing to allow adequate airflow and growth.
Advanced Insights
1. Smart Vertical Gardens
The future of vertical gardening lies in smart technology:
- Automated irrigation systems: Controlled through smartphone apps for precise water management.
- AI-powered plant monitoring: Sensors track plant health, detecting issues like pest infestations or nutrient deficiencies.
- Data analytics: Collecting data on weather patterns and humidity to optimise plant care.
2. Integrating Renewable Energy
Future vertical gardens may incorporate renewable energy sources:
- Solar-powered irrigation systems: Using solar panels to power the drip irrigation.
- Wind turbines in green walls: They generate renewable energy from the wind that flows through the garden.
3. Urban Agriculture and Food Security
Vertical gardens are increasingly being used for urban farming:
- Vertical farms: Growing fruits and vegetables in hydroponic or aeroponic systems.
- Reducing food miles: Enhancing local food production and reducing transportation emissions.
- Improving food security: Supporting urban agriculture in densely populated areas.
The Future of Vertical Gardens
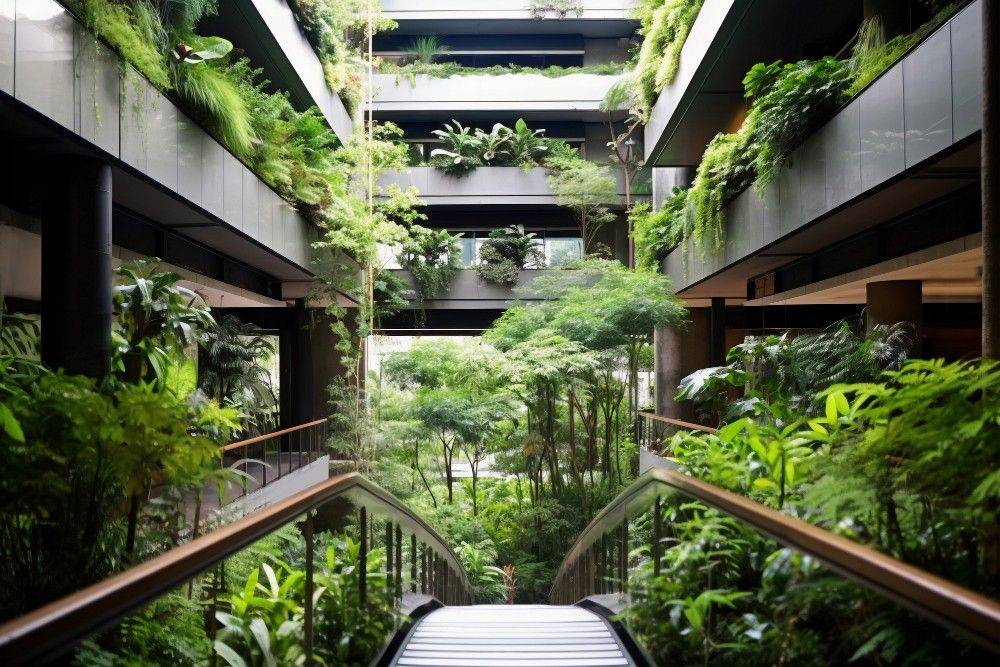

Vertical gardens represent a transformative solution to the challenges of urbanisation. Integrating green architecture into cityscapes helps the environment. It boosts air quality and supports urban biodiversity. As technology gets better, vertical gardens will be smarter, work more efficiently, and be easier to use.
If you live in the city and want more plants at home, vertical gardens are a great choice. They’re also perfect for city planners who want eco-friendly designs. With good planning and the right plants, these living walls will change urban spaces. Proper care helps, too. They will create healthier and more beautiful cities for future generations.
How would you incorporate a vertical garden into your living space or community? Share your ideas and experiences in the comments below!